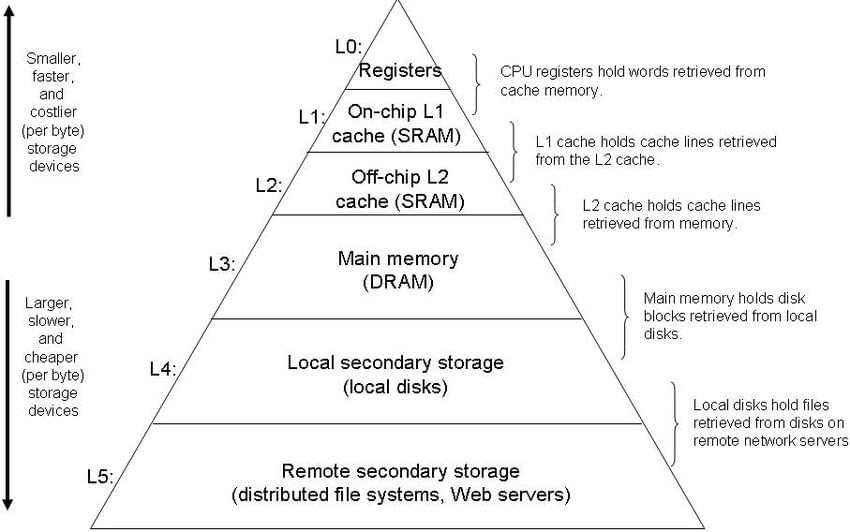
In a previous post, we discussed how the various relational operators are implemented in relational database systems. If you have read that post, you probably still remember that there are a few alternative implementations for every operator. Thus, how should RDBMS determine which algorithm (or implementation) to use?
Obviously, to optimize the performance for any query, RDBMS has to select the correct the algorithm based on the query. It would not be desirable to always use the same algorithm. Also, SQL is a declarative language (i.e., as a programmer we only declare what we want to do with the language, not tell how the language should accomplish the task). Therefore, it would be an anti-pattern if the user of the database system needs to specify which algorithm to use when writing the query. Instead, the correct approach would be that the user would treat the entire system as a blackbox. The end-user should not care about which algorithm is picked but expect the performance optimization is guaranteed.